Type
Sandwich ELISA, HRP-labelled antibody
Description
The Human (Nampt/PBEF) ELISA Kit is to be used for the in vitro quantitative determination of human Visfatin in serum and plasma. This ELISA Kit is for research use only.
Applications
Serum, Plasma
Sample Requirements
100 μl/well
Shipping
On blue ice packs. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the complete kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
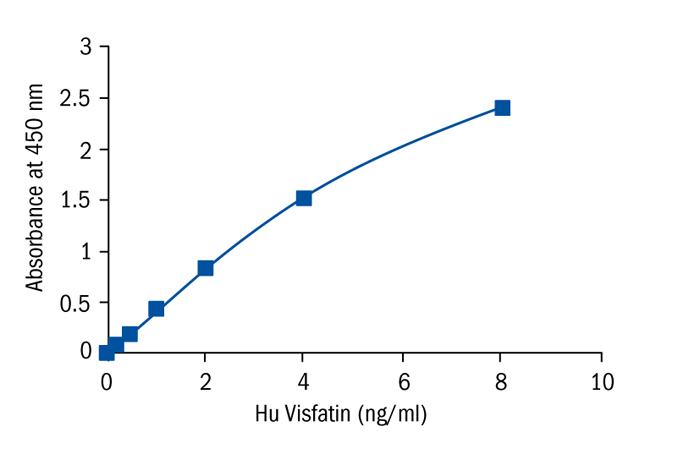
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
0.125 - 8 ng/ml
Limit of Detection
30 pg/ml
Spiking Recovery
98%
Dilution Linearity
85-105%
Physical Appearance
White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder.
Specificity
This ELISA is specific for the measurement of natural and recombinant human Nampt. It does not cross-react with human adiponectin, human resistin, human vaspin, human RBP4, human GPX3, human progranulin, human IL-33, human clusterin, human ANGPTL3, human ANGPTL4, human ANGPTL6, mouse RBP4.
Note
More about Visfatin on BioVendor Scientific Blog
Features
- RUO
- calibration range 0.125-8 ng/ml
- limit of detection 30 pg/ml
Research topic
Cytokines and chemokines and related molecules, Energy metabolism and body weight regulation
Summary
Fukuhara et al. (1) isolated visfatin, an adipocytokine that is highly enriched in the visceral fat of both humans and mice and whose expression level in plasma increases during the development of obesity. Visfatin corresponds to pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF), a 52-kD cytokine expressed in lymphocytes. The gene encoding PBEF was originally isolated from an activated lymphocyte cDNA library (2). Although PBEF lacks a typical signal sequence for secretion, transfected COS-7 and mouse embryonic fibroblasts secreted PBEF into the culture medium. Samal et al. (2) found that recombinant PBEF secreted from transfected COS-7 and mouse embryonic fibroblasts was not itself active in a pre-B-cell colony formation assay, but it synergized the pre-B-cell colony formation activity of stem cell factor and interleukin-7. Jia et al. (3) found that PBEF is an inflammatory cytokine that plays a requisite role in the delayed neutrophil apoptosis of sepsis. Visfatin exerted insulin-mimetic effects in cultured cells and lowered plasma glucose levels in mice. Mice heterozygous for a targeted mutation in the visfatin gene had modestly higher levels of plasma glucose relative to wild type littermates. Surprisingly, it was found that visfatin binds to and activates the insulin receptor (1). However, this original discovery has not been reproduced by two groups (4-5). Visfatin, which is a secretory form of Nampt (nicotinamide phosphoribosyl-transferase), the rate-limiting enzyme of the mammalian NAD, plays a key role in secretion of insulin in the pancreatic beta-cells (5). Recently, two recent studies showed that plasma or serum levels of visfatin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus was elevated (6-7), suggesting that measurement of plasma visfatin provides a relevant tool for understanding metabolic diseases.
Find documents for the lot
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Example Instructions for Use (RUO)
Safety Information (RUO)
MSDS (RUO)